Explain the Different Currents Underlying the Action Potential
The current is distinctively different in both its kinetics and pharmacology from the conventional calcium current described in single. The longitudinal current is determined by the difference in potential between the region where the impulse is at its peak and the region ahead normally resting.
Outward currents are shown as positive and are hyperpolarizing.
. Request PDF A model of the action potential and underlying membrane currents in a rabbit atrial cell We have developed a mathematical model of the rabbit atrial myocyte and have used it in an. Switch to Voltage Clamp. Underlying these action potentials are highly nonlinear voltage-dependent ionic conductances with varying biophysical properties.
Full PDF Package Download Full PDF Package. For example at the resting potential potassium currents flow out of the nerve cell and act to hyperpolarize it. For long steady stimuli like the currents underlying receptor potentials As the duration of the pulse becomes longer than the time constant the total charge is no longer the determining factor.
A short summary of this paper. How does this differ from current clamp. Current and duration values were related exponentially.
How does this differ from current clamp. 2 The membrane begins to depolarize when an external stimulus is applied. Development of ionic currents underlying changes in action potential waveforms in rat spinal motoneurons.
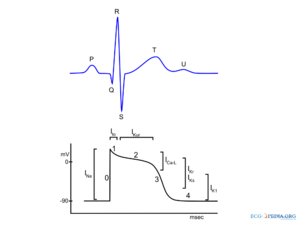
The resulting action potential see figure 6a has a characteristic slow upstroke but a normal large plateau. The resting potential is -60 mV. Calcium cations and chloride anions are involved in a few types of action potentials such as the cardiac action potential and the action potential in the single-cell alga Acetabularia respectively.
This article will discuss the definition steps and phases of the action potential. Compute the absolute refractory period of the neuron. Stages of an Action Potential.
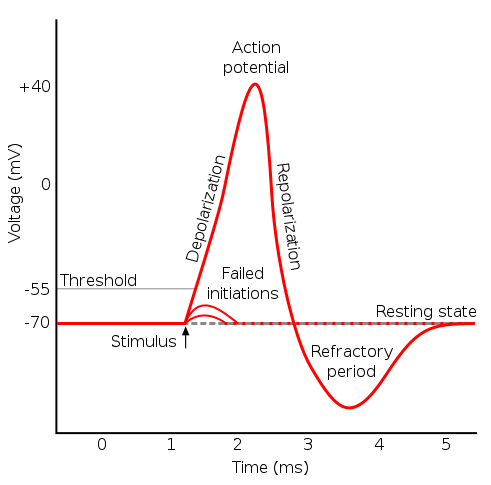
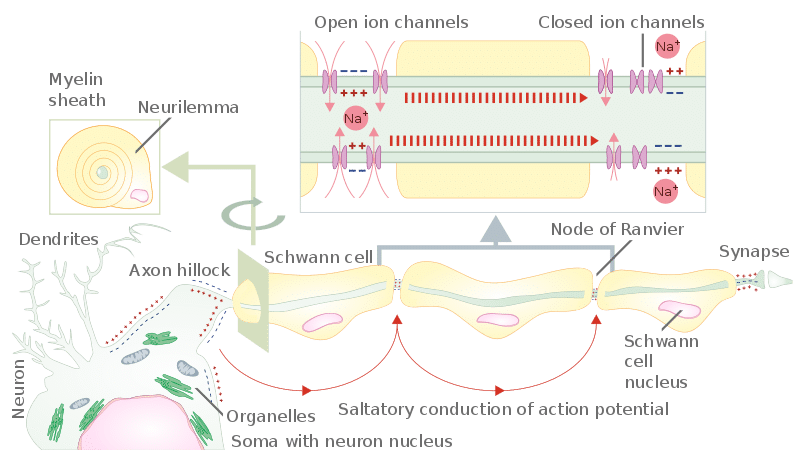
Compute the absolute refractory period of the neuron. V m then repolarizes overshoots the resting membrane potential causing the afterhyperpolarization as the voltage-gated K channels stay open. The depolarisation of the membrane by the action potential generates local currents that depolarise adjacent parts of the axon membrane.
This is probably because in contrast to the situation in Purkinje fibres the ventricular plateau is too positive for the sodium. Find a duration after the first action potential for which a pulse of the same exact amplitude and duration as the initial pulse can again evoke an action potential. For example at the resting potential sodium currents flow into the nerve cell and act to depolarize the nerve cell.
Generation of the action potential is associated with an increase in membrane Na conductance and Na current followed by an increase in K conductance and K current. Before action potential generation Na channels are neither activated nor. No significant difference was noted for inward currents.
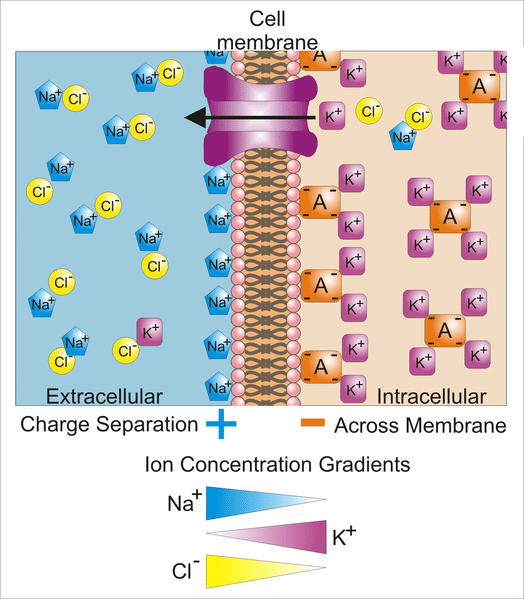
Inactivation is five to ten times longer. In view of the possibility of electrical coupling between endothelial and. Note that the resting potential is not equal to the K equilibrium potential because as discussed previously there is a small resting Na permeability that.
If these local currents depolarise the adjacent membrane to threshold the action potential will be propagated to this part of the membrane and so on down the axon. Author Summary Neurons produce a myriad of action potentials with different shapes and varying heights and widths. Plotting voltage measured across the cell membrane against time the events of the action potential can be related to specific changes in the membrane voltage.
The aim of the present study was to use the approach of Edwards Hirst 1988 to examine the membrane currents underlying the actions of EDHF and importantly to relate these ionic mechanisms to the functional response by simultaneously recording arteriole diameter and membrane potential. Hodgkin and Huxleys reconstruction of the action potential and all its features shows that the properties of the voltage-sensitive Na and K conductances together with the electrochemical driving forces created by ion transporters are sufficient to explain action potentials. Each action potential comes at a cost.
DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY 134 fig-71 1989 Ionic Currents Underlying the Action Potential of Ram pipiens Oocytes LYANNE CHLICHTER Department of Physiology Medical Sciences Building University of. Differentiation of the ionic mechanism underlying changes in action potential properties was investigated in spinal motoneurons of embryonic and postnatal r. 1 At rest the membrane voltage is -70 mV.
Although action potentials are generated locally on patches of excitable membrane the resulting currents can trigger action potentials on neighboring stretches of membrane precipitating a. Threshold potential of -60 mV decreasing to 80 ms at the peak current voltage of -30 mV. Only neurons and muscle cells are capable of generating an action potential.
The Journal of Physiology 2001. An action potential is bounded by a region bordered on one extreme by the K equilibrium potential -75 mV and on the other extreme by the Na equilibrium potential 55 mV. An action potential is defined as a sudden fast transitory and propagating change of the resting membrane potential.
Explain how you determine this. These results suggest that many taste receptor cells conduct action potentials which may be classified broadly into two groups on the basis of action potential duration and potassium current magnitude. Show how you can use voltage clamp and pharmacology to determine the identity of the different currents underlying the action potential.
K currents underlying the action of endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor in guinea-pig rat and human blood vessels. Fast sodium current underlying the rapid upstroke Lee et al. Their use of both empirical and theoretical methods brought an unprecedented level of rigor to a long.
Show how you can use voltage clamp and pharmacology to determine the identity of the different currents underlying the action potential. When the voltage-gated Na channels inactivate and voltage-gated K channels open the action potential peaks between 0 and 40 mV. Now the first pulse in a train will be evoked at the same amplitude regardless of the duration of the pulse since this action potential will be evoked before the pulse is complete.
If the axon is cooled and action potential dwells for a longer time at its peak more longitudinal current will flow. The brain uses a substantial portion of its total energy budget to generate and. Switch to Voltage Clamp.
Change the Stimulus current subsequent pulses to the threshold current you found in question 4A this should be the same value that the Stimulus current first pulse is currently. When these channels close the V m returns to the resting potential. Half steady-state activation and inactivation are at -50 and -45 mV respectively.
Explain how you determine this. That property is called the excitability.
Action Potential The Resting Membrane Potential Generation Of Action Potentials Teachmephysiology

Cv Physiology Non Pacemaker Action Potentials

Membrane Current An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Relationship Between Cardiac Action Potential And Ion Channel Currents Brugada Syndrome Med School Study Syndrome

Action Potential An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Cardiac Action Potential An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

The Ventricular Action Potential With A Description Of The Major Phases Via Behere And Weindling In Annals Of Pe Genetic Abnormalities Pediatrics Major Events

Membrane Current An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Action Potential The Resting Membrane Potential Generation Of Action Potentials Teachmephysiology

Potentiometric Methods A Introduction 1 Potentiometric Methods Based On Measurements Of The Potential O Electrochemical Cell Reference Electrode Lecture

Action Potentials Foundations Of Neuroscience

Membrane Current An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Cardiac Electrophysiology Action Potential Automaticity And Vectors Ecg Echo
Action Potential The Resting Membrane Potential Generation Of Action Potentials Teachmephysiology

Comments
Post a Comment